What is diabetes Mellitus?
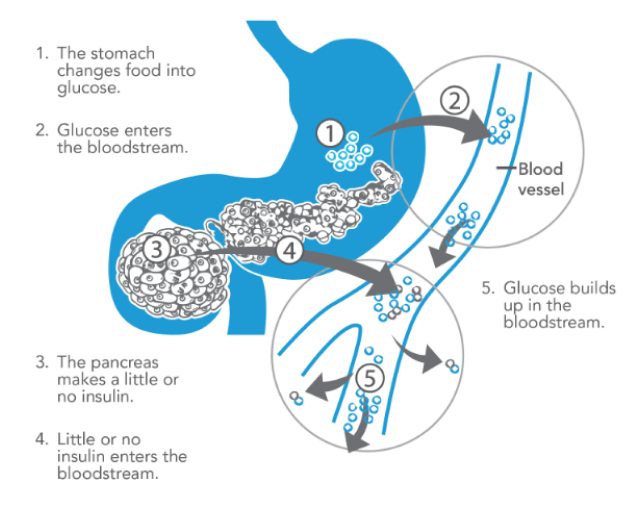
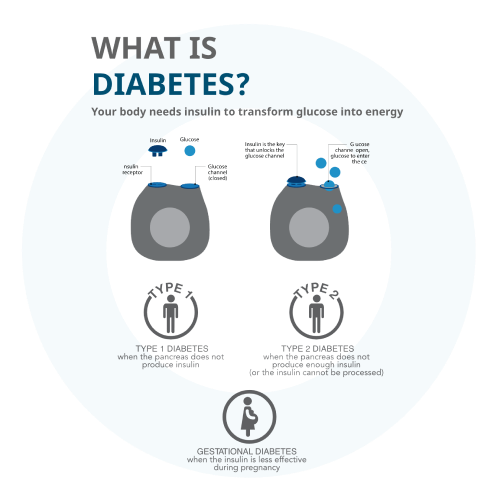
Diabetes mellitus, or simply diabetes, is a chronic disease that occurs when the pancreas is no longer able to make insulin, or when the body cannot make good use of the insulin it produces.

What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas, that acts like a key to let glucose from the food we eat pass from the blood stream into the cells in the body to produce energy. All carbohydrate foods are broken down into glucose in blood and, in turn, insulin helps glucose get into the cells.

What is type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is usually caused by an auto-immune reaction where the body’s defence system attacks the cells that produce insulin. The reason this occurs is not fully understood. People with type 1 diabetes produce very little or no insulin. The disease may affect people of any age, but usually develops in children or young adults. People with this form of diabetes need injections of insulin every day in order to control the levels of glucose in their blood.
What is glucose?
Glucose is a type of sugar produced by the breakdown of carbohydrates during digestion.
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are essential for your diet and are considered the primary source of energy for your body. The end product of digestion of carbohydrates in the body is glucose (or sugar). Therefore, you read the term ‘glucose’ in your blood test reports rather than sugar.
Foods that are considered a rich source of carbohydrates include:
1. Healthy options such as whole grain bread, brown rice, legumes, vegetables, fruits, milk, yoghurt, etc.
2. Unhealthy options such as sweets, desserts, regular soft drinks, etc.
Types of carbohydrates
1. Simple carbohydrates: Also known as sugars, these are found in two forms:
- Natural sugars such as in milk, fruits and vegetables. These are your healthier options because they contain other nutrients including vitamins and fibre.
- Added sugars during food processing or refining. These are found under different names such as brown sugar, corn syrup, fructose, glucose and high-fructose corn syrup.
2. Complex carbohydrates: These are made of multiple sugars and include two types:
- Starch: Mainly found in grains (such as rice, wheat, oats, etc.) and starchy vegetables (such as potatoes, corn, and peas).
- Dietary fibres: Also known as roughage, these include plant parts that cannot be digested by the enzymes of your body. These can be mainly found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes. Fibres can significantly slow down the absorption of carbohydrates and help in improving your blood glucose levels. Therefore, you must ensure that you include plenty of high-fibre foods in your daily diet.
Food and drinks containing carbs:



Foods containing little or no carbohydrates:


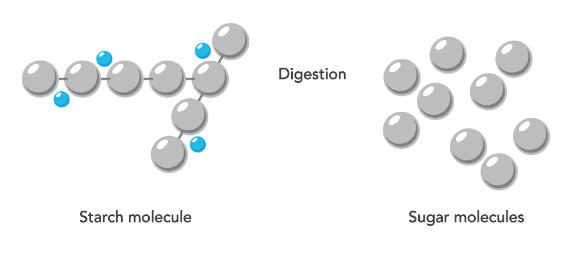
Digestion of carbohydrates
The foods that you consume every day help you remain healthy, while also supplying you with the energy you need for your daily activities. Food comprises three main types of nutrients: carbohydrates, protein and fats. Carbohydrates have the most direct impact on your blood glucose levels. When the pancreas senses the presences of glucose in the blood, it secretes insulin. Insulin is the hormone that works like a key and unlocks the body cells allowing glucose to enter and be used as energy

Gylcaemic Index
The Glycaemic Index is a scale that measures how foods containing carbohydrates can cause a surge in the blood-glucose level. Foods with a score of 70 or higher are defined as having a high glycemic index, while those with a score of 55 or below possess a low glycemic index.
LOW GI : beans peas lentils rye bread apples oranges
HIGH GI : white bread potatoes puffed cereals mango
Replacing high GI carbs with low GI carbs in complex meals leads to improved clinical outcomes for people with type 1 diabetes.

Counting Carbs
1. Introduction
As carbohydrates have the most direct impact on your blood glucose levels, it is very important to control the quantity and quality of carbohydrates that you consume.
2. What is carbohydrate counting?
Carbohydrate counting is a practical technique that helps you calculate the carbohydrate content in your meals. Learning about foods that contain carbohydrates is imperative because carbohydrates have the most immediate impact on your blood glucose levels.
3. In order to learn carbohydrate counting you should:
Carbohydrate counting is a practical technique that helps you calculate the carbohydrate content in your meals. Learning about foods that contain carbohydrates is imperative because carbohydrates have the most immediate impact on your blood glucose levels.
- Be able to read and write
- Be able to work out simple math calculations
- Frequently visit the dietitian
- Be able to understand food labels
- Be willing to keep adequate records
4. What are the benefits of counting carbs?
- Helps in planning your meal
- Allows you to ensure a tighter control of your blood glucose
- levels
- Helps you estimate the amount of insulin needed for the food
- consumed
- Allows you greater flexibility in choosing your meals
5. Tools used in counting carbs
- Food scale
- Measuring cups for liquids and solids
- Measuring spoons
- The Handy Hand guide
- Food label
- Personal food diary
- Nutrition books
- Online resources
- Smart phones apps
6. How to count carbohydrates?
There are primarily two methods to count your carbs:
- Carb Exchange System: in which 1 exchange (serving) = 15 grams of carbs
- Carb gram counting: using the carbohydrate factor for carb rich foods multiplied by (x) the weight of the food consumed
Your Food Weight x Food FACTOR = Grams of Carbohydrates in that Food
For instance,
Bread: white, rye, whole wheat (48-50% by weight carbs; carb factor is around 0.48) 30 grams weight of 1 toast slice x 0.48 = 14.4 ~ 15 gram carbs
7. Levels of carbohydrate counting
- Basic carb counting includes eating a consistent number of carbs each day
- Advanced carb counting
8. How much carbohydrate do you need to include in your diet every day?
The number of carbs you need usually depends on your medication and weight goals - nonetheless, generally:
- Most men need: 4-5 carb servings at each meal
- Most women need: 3-4 carb servings at each meal
- Only if hungry, snack (optional): 1-2 carb servings

The Hand Guide
You can stay on track by using this quick guide to estimate your portion sizes when you cannot, or prefer not, to measure your food. Use the hand guide to estimate how much you consume.
 Thumb tip
Thumb tip
- 1 serving or 1 tsp olive oil
 Thumb
Thumb
- 1 serving or 30 g low fat cheese
 Fist
Fist
- 3 servings or 9 tbsp pasta or rice
 Palm with the thickness Of your little finger
Palm with the thickness Of your little finger
- 3 servings or 90 g cooked meat
 Handful
Handful
- 1 serving or 30 g nuts

Nutrition label
- Is a label found in most packaged food that includes nutrition guides for educational purposes an general health.
- It provides you with the necessary information to know exactly what you’re eating.
Benefits of Nutrition Label
- It lists the ingredients and the nutritional information of a certain food product.
- It helps estimate portion sizes and compare these with what you consumed - the serving sizes are also provided.
- It helps estimate the number of calories in the food product.
- It enables comparisons of similar food products with a focus on fibre, carbs, fat and caloric content.